Effect of Cu-Rich Phase Precipitation on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrNiCux Medium-Entropy Alloys Prepared via Laser Directed Energy Deposition
富铜相沉淀对激光定向能量沉积制备的 CoCrNiCux 中熵合金组织和力学性能的影响
レーザー指向性エネルギー堆積によって調製されたCoCrNiCux中エントロピー合金の微細構造と機械的性質に及ぼすCuリッチ相析出の影響
레이저 유도 에너지 증착을 통해 제조된 CoCrNiCux 중간 엔트로피 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 대한 Cu-풍부 상 침전의 영향
Efecto de la precipitación en fase rica en Cu sobre la microestructura y las propiedades mecánicas de las aleaciones de entropía media CoCrNiCux preparadas mediante deposición de energía dirigida por láser
Effet de la précipitation de phase riche en Cu sur la microstructure et les propriétés mécaniques des alliages à entropie moyenne CoCrNiCux préparés par dépôt d'énergie dirigé par laser
Влияние осаждения богатой медью фазы на микроструктуру и механические свойства сплавов со средней энтропией CoCrNiCux, полученных методом лазерного наложения энергии
レーザー指向性エネルギー堆積によって調製されたCoCrNiCux中エントロピー合金の微細構造と機械的性質に及ぼすCuリッチ相析出の影響
레이저 유도 에너지 증착을 통해 제조된 CoCrNiCux 중간 엔트로피 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 대한 Cu-풍부 상 침전의 영향
Efecto de la precipitación en fase rica en Cu sobre la microestructura y las propiedades mecánicas de las aleaciones de entropía media CoCrNiCux preparadas mediante deposición de energía dirigida por láser
Effet de la précipitation de phase riche en Cu sur la microstructure et les propriétés mécaniques des alliages à entropie moyenne CoCrNiCux préparés par dépôt d'énergie dirigé par laser
Влияние осаждения богатой медью фазы на микроструктуру и механические свойства сплавов со средней энтропией CoCrNiCux, полученных методом лазерного наложения энергии


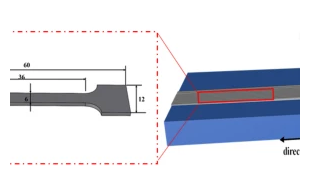
Reviews and Discussions
